Momentum is a vector which means it has both direction and magnitude. Thi is because it is calculated using an object's _____ rather than its speed. Momentum is calculated by multiplying an objects mass by its velocity:
| p = mv | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
where |
p | = | Momentum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| m | = | Mass | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| v | = | Velocity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
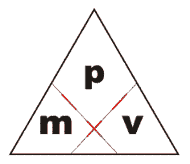
This can be summarised in the following 'magic triangle':

The units of mementum do not have their own symbol or name, instead they are a combination of the units of mass and velocity multpilied, ie:
Kg m/s = Kg ms-1
The principle of "The Conservation of Momentum" tells us that the total momentum before a collision equals the total momentum after the collision. We can use this to find the velocity of objects after a collision.

