Thursday 4th September
TODAY WE ARE
LEARNING ABOUT
LEARNING ABOUT
TODAY'S
KEY WORDS ARE
KEY WORDS ARE

Memory Anchor:
YOU WILL SHOW
YOUR LEARNING BY...
YOUR LEARNING BY...
- Students to sort prepared slides or diagrams of unicellular organisms based on their characteristics.
Super Challenge:
Stretch:
Challenge:
Key Questions:
- What does unicellular mean?
- UniCellular organisms are living things made up of only a one Cell.
- What does multicellular mean?
- MultiCellular organisms are living things made up of many Cells.
- Name 3 types of unicellular life.
- Bacteria, Protozoa and Yeast are examples of uniCellular organisms.
- What are the parts of a bacterial cell?
- A bacterial Cell consists of cytoplasm and a membrane surrounded by a Cell wall; the genes are not in a distinct nucleus. Some Bacteria may have Flagella (tails) to swim.
- What organelles do yeast cells have?
- Yeast Cells have a nucleus, cytoplasm and a membrane surrounded by a Cell wall.
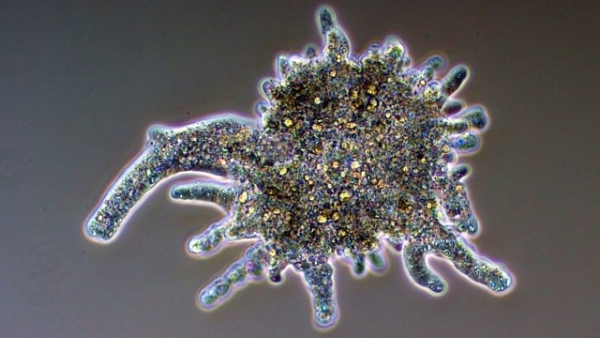
- What are pseudopodia?
- Protoza have pseudopodia (“false feet”) to move about and to surround food and take it inside the Cell. Protoza have temporary vacuoles containing waste.
- Can you see unicellular or multicellular organisms with the naked eye?
- You can see multiCelluar organisms with the naked eye. Most uniCellular organisms are too small to see without a microscope.
