Thursday 4th September
TODAY WE ARE
LEARNING ABOUT
LEARNING ABOUT
TODAY'S
KEY WORDS ARE
KEY WORDS ARE

Memory Anchor:
YOU WILL SHOW
YOUR LEARNING BY...
YOUR LEARNING BY...
Super Challenge:
Stretch:
Challenge:
Key Questions:
- How can an insect pollinator transfer pollen from one flower to another?
- insect pollination: - Insects attracted to petals and nectar. - Insect enters flower and pollen is transferred from Anther to Insect. - Insect is attracted to another flower. - Pollen from Insect is transferred to Stigma. - Pollen Cell grows a pollen tube down the Style to the Ovary.
- What happens to cause fertilisation in a flower?
- Fertilisation occurs when the Pollen nucleus fuses with the Ovule. The fertilised Ovule forms the seed. The Ovary forms the Fruit.
- What is the role of a pollen cell?
- The function of Pollen Cells are to transfer genetic material (DNA) from one plant to another.
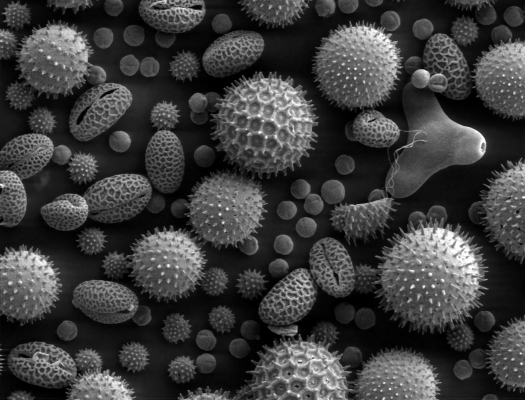
- How are pollen cells adapted - Give at least 2 ways.
- Pollen Cells are adapted to their function by: - being small (microscopic) - having a tough outer coating - can have spikes or hooks
- Why does pollen have a tough outer coating? Why do some pollens have spikes or hooks on them?
- Pollen being small allows it to be transported easily by insects (and wind next lesson) Pollen having a tough outer coating allows the Cell to survive in the environment away from the plant. Pollen have spikes or hooks makes it more likely to stick to insects.
