Saturday 6th September
TODAY WE ARE
LEARNING ABOUT
LEARNING ABOUT
TODAY'S
KEY WORDS ARE
KEY WORDS ARE

Memory Anchor:
YOU WILL SHOW
YOUR LEARNING BY...
YOUR LEARNING BY...
Super Challenge:
Stretch:
Challenge:
Key Questions:
- Are all rocks the same age?
- There are lots of different rocks of all sorts of ages.
- Where are the oldest rocks found?
- The oldest rocks are found in Africa, Canada and Australia.
- Where are the youngest rocks on the earth generally found?
- The youngest rocks are found around volcanoes.
- Why has the amount of rock material on the earth remained fairly constant since its formation?
- No new material gained or lost from the planet (with the exception of the small number of meteorites that have collided with the planet)
- What materials are new rocks made from?
- Those recycled by the earth over its existence.
- What type of rocks are formed when molten rock freezes?
- Igneous rocks
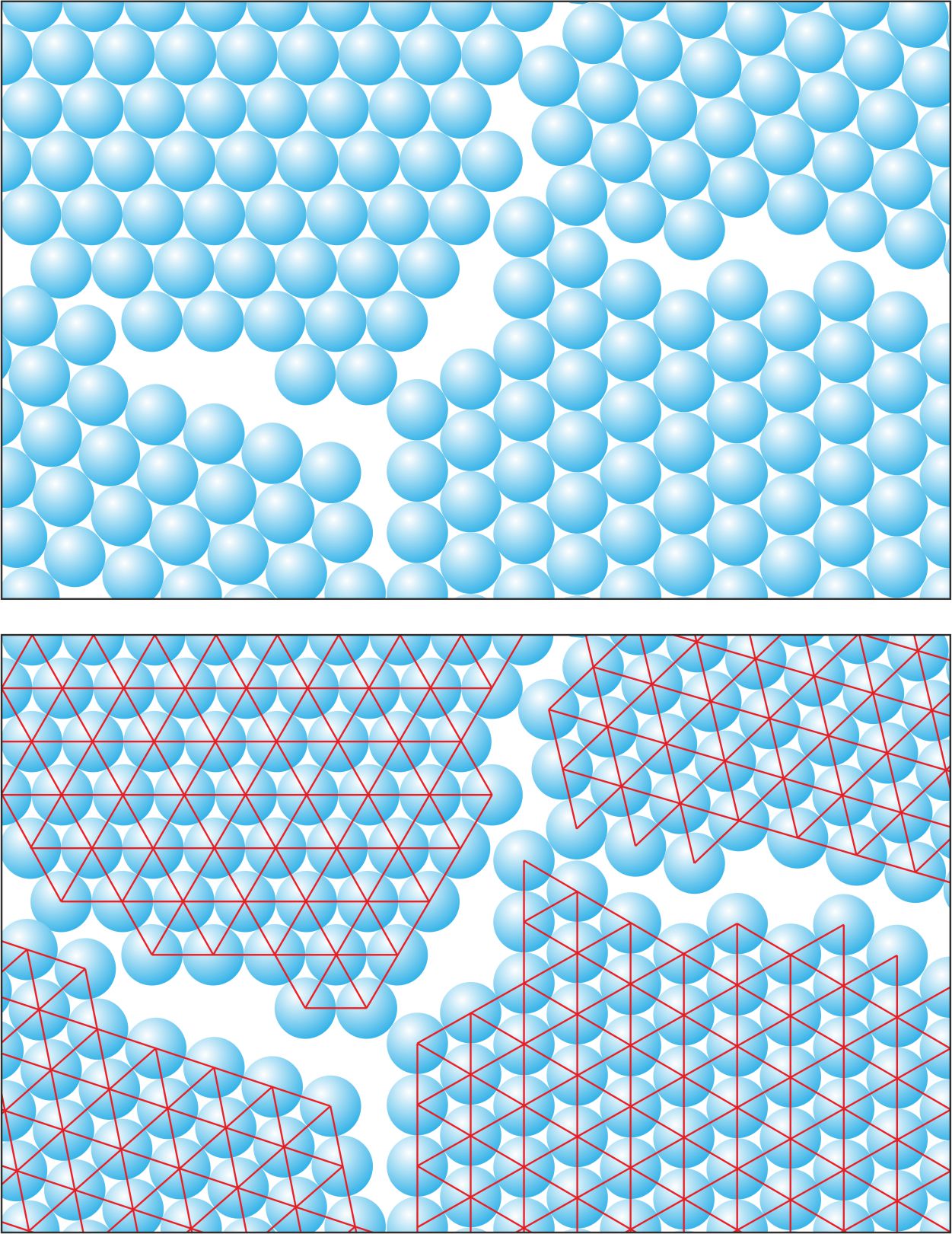
- Describe the structure of particles in an igneous rock
- Particles in an igneous rock are fixed in a lattice, the reason why the rocks hold their shape.
- Solids are made up of crystals. What are crystals?
- Crystals are regions of a single lattice orientation.
- How does the rate at which something freezes affect the size of the crystals it contains?
- The slower the rate of freezing, the greater the size of the crystals that are formed within that structure.
- Why are the crystals formed larger when an object freezes more slowly?
- The crystals are large because the Particles have more time to line up before freezing.
- Why are the crystals formed smaller when an object freezes quickly?
- The crystals are small because the Particles have less time to line up before freezing.
- What size crystals are formed when solids freeze slowly?
- When solids freeze slowly the crystals are large.
- What is the impact on the structure of an igneous rock when it forms slowly under the ground?
- Due to it cooling slowly, it will contain large crystals.
- What is the impact on the structure of an igneous rock when it forms above the ground or in water, resulting in tit cooling rapidly?
- Due to it cooling quickly, it will contain small crystals.
- Does the size of crystals affect the properties of a rock?
- The size of crystals affects some of the properties of the rock.
