Saturday 6th September
TODAY WE ARE
LEARNING ABOUT
LEARNING ABOUT
TODAY'S
KEY WORDS ARE
KEY WORDS ARE

Memory Anchor:
YOU WILL SHOW
YOUR LEARNING BY...
YOUR LEARNING BY...
Super Challenge:
Stretch:
Challenge:
Key Questions:
- What is the structure and function of each of the following: a) heart, b) lungs?
- The structure and function of the heart and lungs are: a) Heart - muscle, 4 chambers, left and right side, function is to pump blood around the body. b) lungs - large surface area, gas exchange surface.
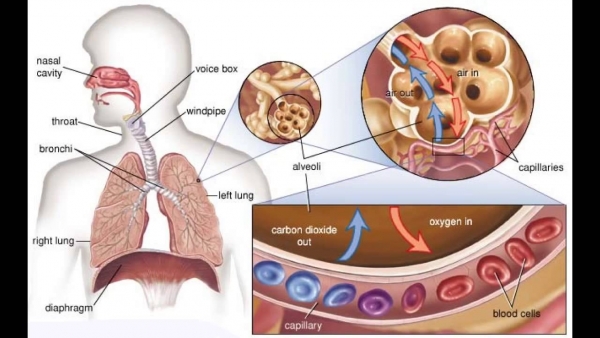
- How are lungs adapted for gaseous exchange?
- The lungs are adpated for gas exchange as they have a large surface area, moist lining, copious blood supply, maintain concetration gradient (ventilation and blood moving through), short diffusion distance.
- How is blood pumped around the body in the human circulatory system?
- The blood is pumped around the body in a double circulatory system.
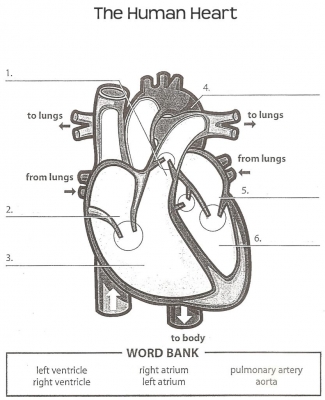
- Where does the left ventricle pump blood to and where does the right ventricle pump to?
- The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs where gas exchange takes place. The left ventricle pumps blood around the rest of the body.
- What are the names and functions of the blood vessels in the heart?
- The main structures in the heart and their functions are: Aorta: a thick walled artery that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body Vena Cava: a thinner walled vein that carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart Pulmonary artery: a thick walled artery that carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart to the lungs Coronary arteries: carry oxygenated blood to the heart muscle
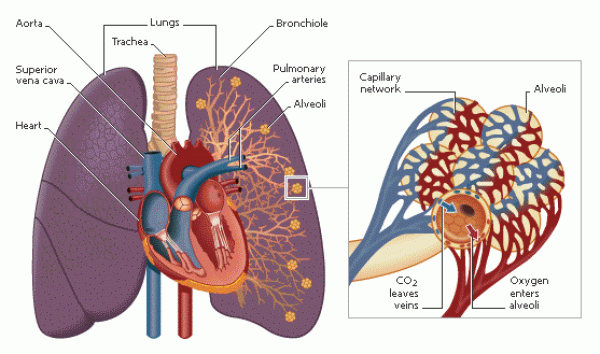
- What are the names and functions of the main structures in the lungs?
- The main structures in the lungs and their functions are: Trachea: is a wide, hollow tube that connects the larynx (or voice box) to the bronchi of the lungs Bronchi: main passage of air into the lungs Alveoli: tiny sacs with large surface area that allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to move between the lungs and bloodstream Capillary network: very thin blood vessels that surround the avleoli for rapid gas exchange
- What controls the natural resting heart rate?
- The natural resting heart rate is controlled by a group of Cells located in the right atrium that act as a pacemaker.
- What are artificial pacemakers?
- Artificial pacemakers are electrical devices used to correct irregularities in the heart rate.
