Friday 5th September
TODAY WE ARE
LEARNING ABOUT
LEARNING ABOUT
TODAY'S
KEY WORDS ARE
KEY WORDS ARE

Memory Anchor:
YOU WILL SHOW
YOUR LEARNING BY...
YOUR LEARNING BY...
Super Challenge:
Stretch:
Challenge:
Key Questions:
- (HT only) How are radio waves produced?
- (HT only) Radio waves are produced by oscillations in electrical circuits.
- How can electromagnetic waves be generated?
- Changes in atoms and the nuclei of atoms can result in electromagnetic waves being generated
- What types of waves are hazardous on human body tissue.
- X-rays and gamma rays can have hazardous effects on human body tissue.
- How are gamma rays generated?
- Gamma rays are emitted from the nucleus. They have no charge or mass.
- What effects can Ultraviolet waves cause to the skin?
- Ultraviolet waves can cause skin to age prematurely and increase the risk of skin cancer.
- What are three ways that show energy is transferred by electromagnetic waves?
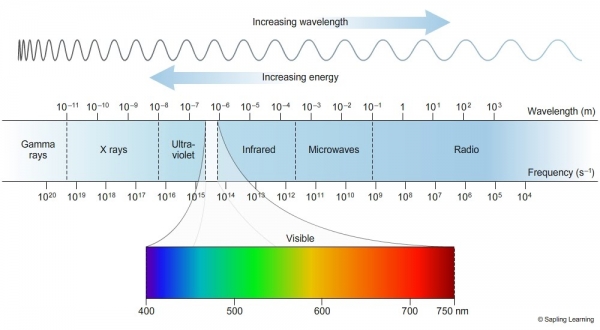
- Some examples of how electromagnetic waves transfer Energy are: Radio waves - radios in communication Microwaves - ovens for heating food Infrared radiation - wireless remote controls Ultraviolet - Ultrasound scans Visible light - heat and light from light bulb X-Ray: Energy passes through tissue but stopped by bone in X ray imaging Gamma: Energy used to kill pathogens during sterilisation of medical equipment
- What effects the outcome of being exposed to radiation?
- The type of radiation and the size of the dose.
- What are the risks and consequences of exposure to radiation?
- The risks of exposure to radiation can include radiation poisoning and cancer.
- What type of electromagnetic waves are ionising?
- X-rays and gamma rays are ionising radiation that can cause the mutation of genes and cancer.
- (HT only) What type of current is produced when radiowaves are absorbed?
- (HT only) When radio waves are absorbed they may create an alternating current.
- (HT only) How can the wavelength of electromagnetic waves be varied?
- (HT only) Different substances may absorb, transmit, refract or reflect electromagnetic waves
- What units is radiation measured in?
- Radiation dose is measured in sieverts
- How many millisieverts are there in 1 sievert?
- 1000 millisieverts (mSv) = 1 sievert (Sv)
- (HT only) Why is each type of electromagnetic wave suitable for practical application?
- Each member of the electromagnetic wave is suitable for a practical application because it has a small range of frequency and wave length.
