The ripple tank allows us to see the behaviour of waves in different situations.
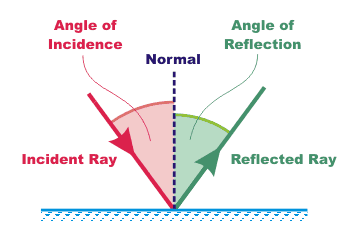
When water waves hit a barrier (something solid) it is reflected so that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence.

Water waves travel slower in shallow water than in deep. This is why waves break. The bottom of the waves slows down as the water becomes shallower up the beach. The top of the wave continues at its original speed and so 'falls' forward.
If wave hits a boundary that will change its speed, it may change direction. The rays will be bent at that boundary. This is called refraction.

When waves Slow down they bend towards the normal.
When waves Speed up they bend away from the normal.
If the waves hit the interface square on (at 90° to the interface) there will be no bending as the whole wave front changes speed at the same time.
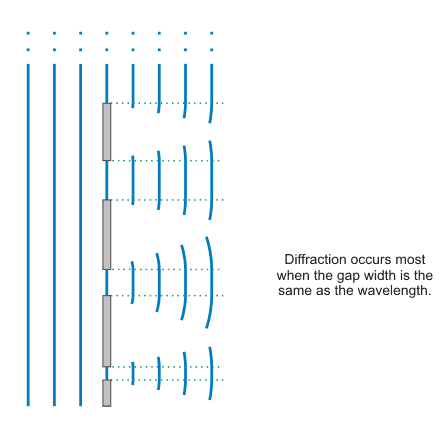
When a wave moves through a gap, or past an obstacle, it spreads out from the edges. This is diffraction.