In the exam use the chemical symbols to represent atoms rather than circles eg:
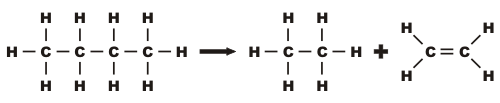
This process involves heating the hydrocarbons to vaporise them and passing the vapours over a hot catalyst. A catalyst is a chemical that speeds up a reaction without being used up or changed itself and allows the reaction to happen at a cooler temperature.